Experiments on deflection using simple capabilities
Center of Gravity or Mass: Try to suggest a new idea
Help for KaderFrame V3-2022 -1
Help for KaderFrame V3-2022 -2
Structure (1) - Example on the reactions
Effect of Wind
Continuity and beam deflection
Effect of the type of support on the deformation shape and the B.M.D
Deformation Shape of a cantilever and a frame due to concentrated load
Design of Concrete Column Program - Free Download (the link is below)
Structure (1) - The civil engineer and what he can do المهندس المدنى وما يمكنه عمله
Structure (1) - Loads-1
Structure (1) - Loads-2
Structure (1) - Supports and Reactions-1
Structure (1) - Supports and Reactions-2
Structure (1) - Stability and Determinacy-1
Structure (1) - Stability and Determinacy-2
Structure (1) - Stability and Determinacy-3
Structure (2) - Properties of Sections
Structure (2) - Straining Actions
Structure (2) - Normal Stresses-1
Structure (2) - Normal Stresses-2
Structure (2) - Normal Stresses-3
Structure (2) - Normal Stresses-4
Structure (2)A - 1 - Introduction
Theory of Structures (2)B - 1 -Introduction
Computer Appl 20 1
2.1 Introduction
192.2 Assumptions
202.3 Sign convention
212.3.1 Sign convention for displacements
212.3.2 Sign convention for forces
212.4 Derivation of the element stiffness matrix
222.4.1 Plane frame element
232.4.2 Beam element
272.4.3 Truss (bar) element
282.5 Loads between nodes
292.6 Transformation matrix
302.7 Element stiffness matrix in global coordinates
332.8 Applications
391.1 Advantages of steel as a building material
11.2 Disadvantages of steel as a building material .
21.3 Comparison between steel and RC structures
21.4 Field of steel structures
21.5 Specifications and Codes
41.6 Structural steel
51.7 Classification of cross sections
51.8 Types of steel cross sections
62. Steel hanger
92.1 Steps for the design of steel hanger
92.2 Choice of the system
92.3 Drawing of the general layout
112.3.2 Bracing system (Wind bracing)
132.3.3 Covering system
152.3.4 Finising
152.4 Calculation of loads and internal forces
332.4.1 Cases of loading
332.4.2 Loads
342.4.3 Internal forces
412.4.4 Design forces (Critical forces)
462.5 Design of structural elements
492.5.1 Buckling
492.5.2 Allowable stresses
542.5.3 Factor of safety and its reasons
552.5.4 Sections used in different members
642.5.5 Design of tension members
652.5.5.1 Choice of section of tension members
682.5.6 Design of compression members
802.5.6.1 Allowable stresses in compression members
802.5.6.2 Choice of section of compression members
812.5.6.3 Tie (Batten) plates
822.5.6.4 Slenderness ratio of Battened compression members
832.5.7 Design of zero members
882.5.8 General considerations for the choice of members
882.6 Design of connections
902.6.1 Methods of connection in steel structures
902.6.2 Bolted connections
902.6.3 Welded connections
1122.7 Drawing of details
124The program tries to help you to test your basic engineering knowledge’s. In version 1.0, there are 100 questions about units, definitions, etc… The arrangement of the questions as will as the answers is random. In each question, there are four answers; one of them either wrong or doesn’t agree with the definition, try to find out this odd answer. If you do well from the first time your degree will be 100% in this question. If not your maximum degree will be reduced by 25% and so on. You will see the total degree for all previous questions.
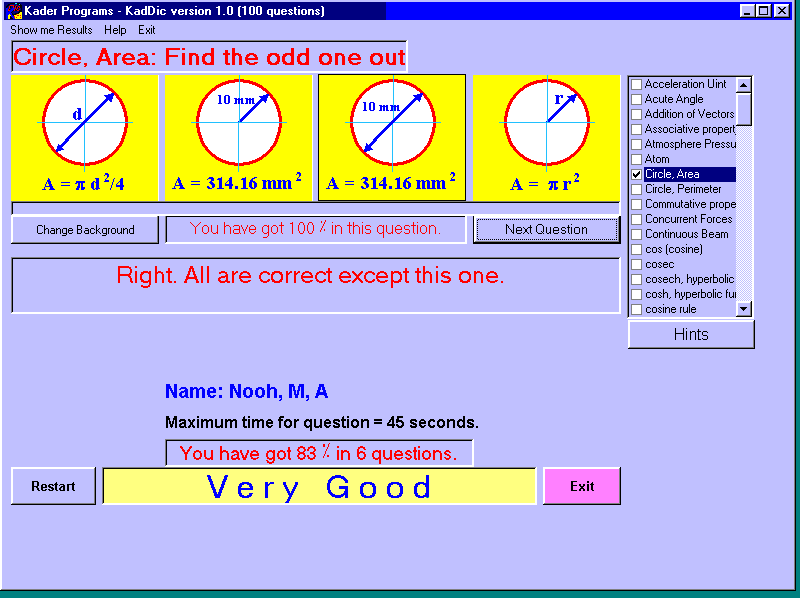
The program tries to help you to test your basic engineering knowledge’s. In version 1.0, there are 100 questions about units, definitions, etc… The arrangement of the questions as will as the answers is random. In each question, there are four answers; one of them either wrong or doesn’t agree with the definition, try to find out this odd answer. If you do well from the first time your degree will be 100% in this question. If not your maximum degree will be reduced by 25% and so on. You will see the total degree for all previous questions.
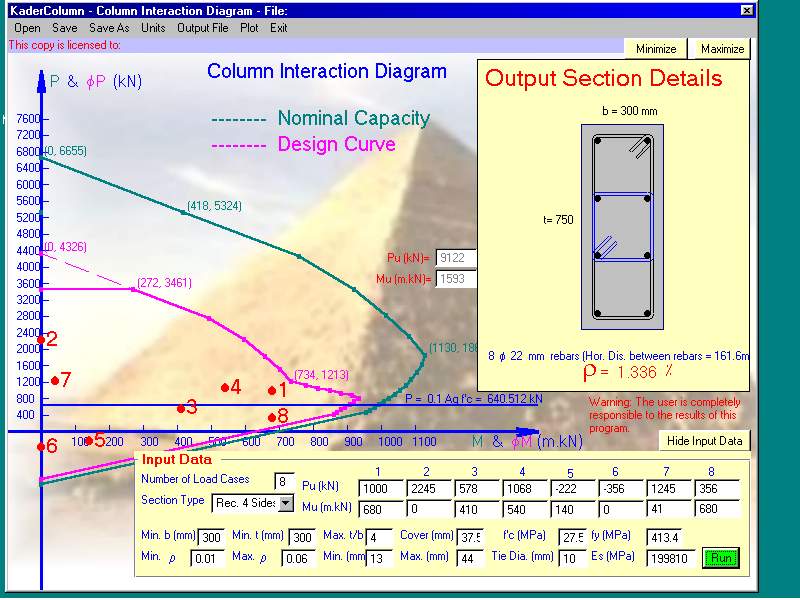
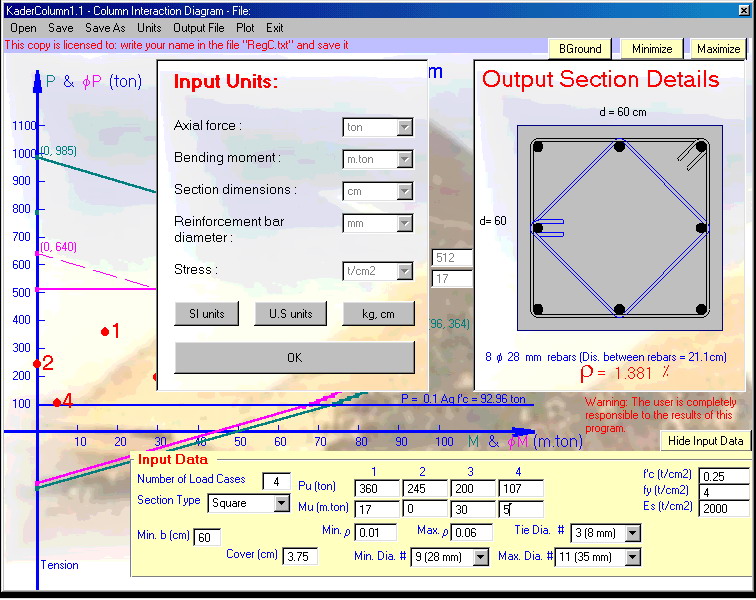
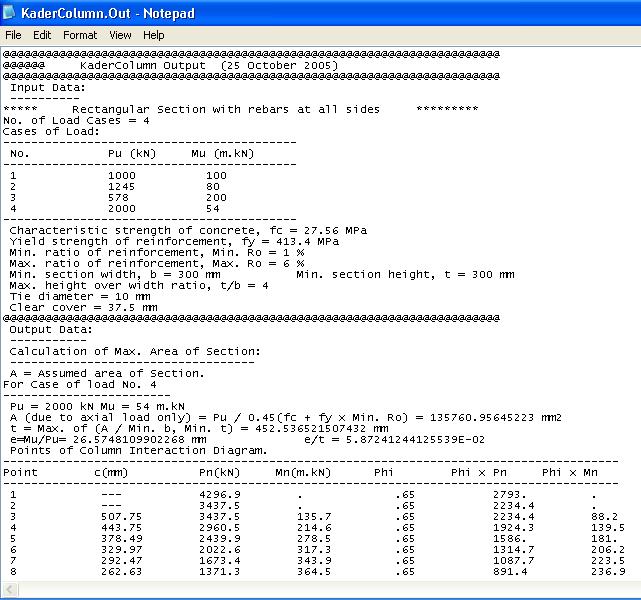
The program deals with tied short columns. It designs columns subjected to up to six cases of loading consisted of axial load and bending moment applied about the maximum principle axis. The program constructs the column strength interaction diagram (Bending moment-Axial load curve and check if all input cases of loading being within the design curve. If the input data of the cross-section is not sufficient the program increases them starting from the Min. Roh to the cross-sectional dimensions until all input cases of loading being within the design curve. The program suggests an arrangement of ties and draws them. (US and SI units)
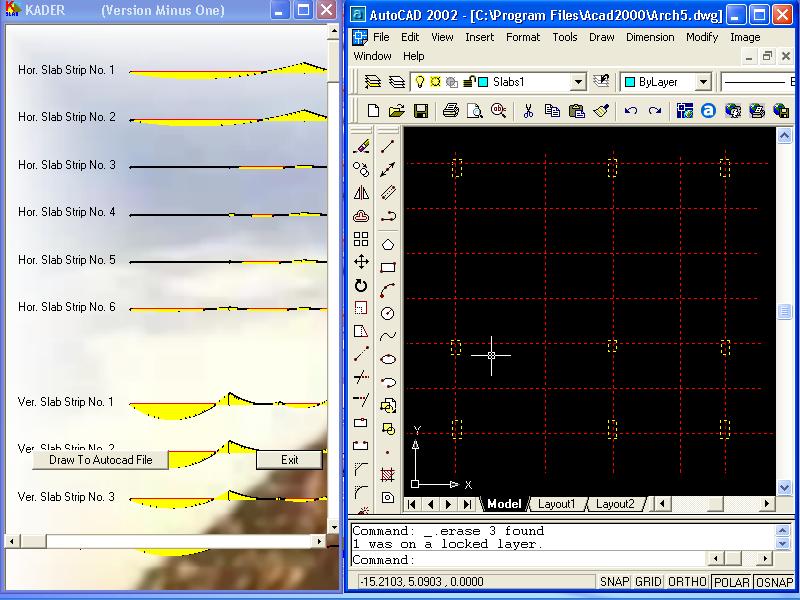
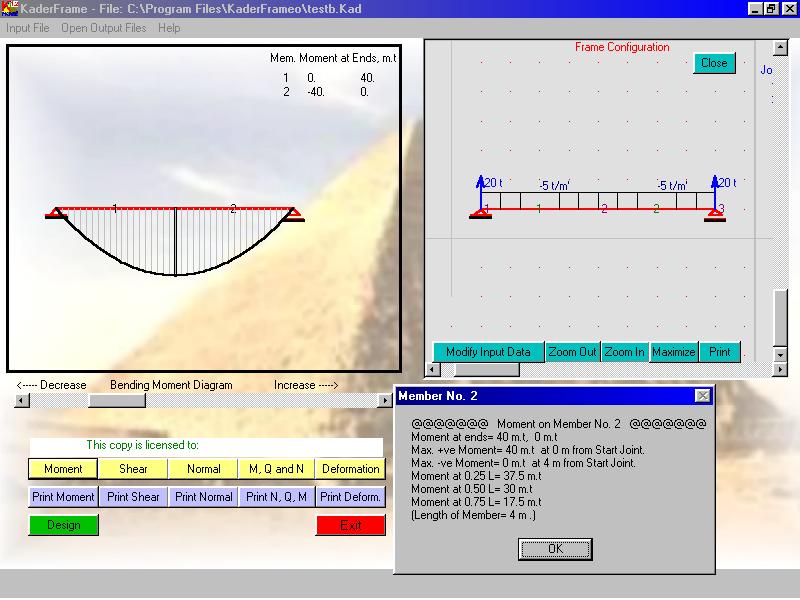
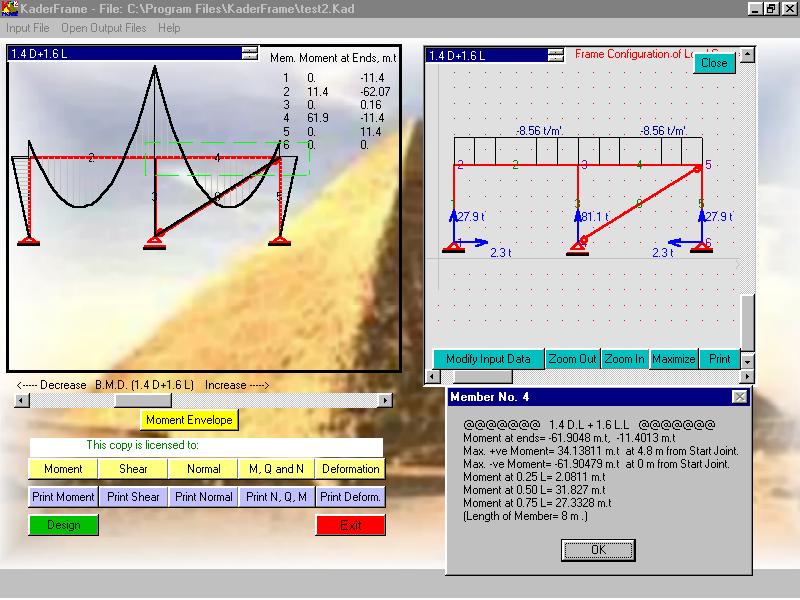
The program solves plane frames and continuous beams. It calculates the normal forces, shearing forces, and bending moments, draws and prints their diagrams. It also draws and prints the deformation shape. Text files of most calculated data are created on the same directory of the program. The program designs the sections byworking stress method and draw the frame and its sections to AutoCad 2000 file. The user can modify the design sections before and of course after drawing to AutoCad file. Only Metric system is used in this version.
The program tries to help you to test your basic engineering knowledge’s. In version 1.0, there are 100 questions about units, definitions, etc… The arrangement of the questions as will as the answers is random. In each question, there are four answers; one of them either wrong or doesn’t agree with the definition, try to find out this odd answer. If you do well from the first time your degree will be 100% in this question. If not your maximum degree will be reduced by 25% and so on. You will see the total degree for all previous questions.
The program tries to help you to test your basic engineering knowledge’s. In version 1.0, there are 100 questions about units, definitions, etc… The arrangement of the questions as will as the answers is random. In each question, there are four answers; one of them either wrong or doesn’t agree with the definition, try to find out this odd answer. If you do well from the first time your degree will be 100% in this question. If not your maximum degree will be reduced by 25% and so on. You will see the total degree for all previous questions.